Tips to Learn Design Without Going to a Design School
Didn’t get the chance to attend a design school? You’re not alone as many barriers can stand between students to achieve their goal to learn design by getting a design degree. Amongst these barriers, the high tuition costs and lack of local design schools are considered the most challenging obstacles that prevent many students from fulfilling their passion for learning design properly.
While the design schools are very important to build coherent design skills that that can help fulfilling the market needs, this doesn’t mean there is no hope of students to learn design. The good news is that alternative learning methods have evolved in the last years including but not limited to MOOCs online courses, YouTube channels, and tutorial website like Designorat here.
Related articles:
- What Designers Need to Learn Aside from Their Design Education
- Can We Apply Design Thinking in Education?
- What Designers Think About Design Education in the Middle East Region
While many designers are using these resources either to learn design from scratch or improve their current skills. However, the observation indicates that students who depend on the online resources to learn design always find a gap in their knowledge such as focusing on the tools rather than the theory and principles of design behind it or learn design from an untrusted source that presents misleading information. While the design schools present coherent learning structure through a complete curriculum that student attend for 2-4 years to get their degree, this structure is not available in the self-learning methods.
How Students Learn Design in Schools
The challenge here is how to help students to properly learn design in order to fulfill their passion to it and prepare their skills for the market needs? In order to address this challenge, we need to understand the structure of the design education in schools. The design curriculum offered in the schools aims to cover a number of theoretical and practical knowledge that are needed to prepare a good designer in a specific field. Accordingly, the courses offered in design schools contribute to building the student’s strengths in three main axises:
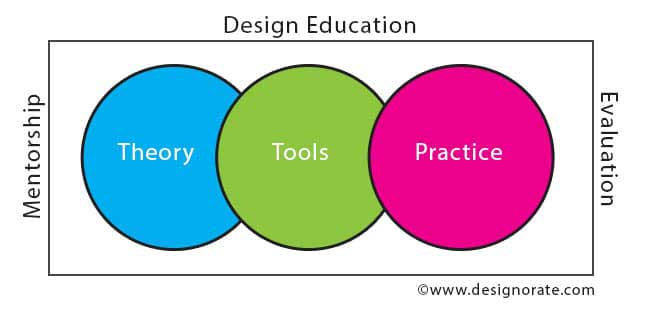
Theory – in this axis, the students learn the principles of design and the related theories that help them to understand the different design challenges and develop coherent solutions for it. The theory may include topics such as the design principles, the gestalt principles, and the color theory.
Tools – Here, the students start to learn the tools that they need to turn their ideas into physical or digital projects. These tools include prototyping tools, digital design applications, and working with different creative media.
Practice – The practice is a main component in the above two axes. In each course, students practice both the theory and tools in a form of academic projects to understand and evaluate their exposure to the knowledge they acquired.
The above three axises are then framed inside the educational process based on two main components; mentorship and evaluation. The mentorship for the course instructor helps the students to build their skills through a structured plan and get help and advice during the course. The evaluation is a process that ensures that students absorbed the required knowledge for a specific topic by grading their projects and activities during the course.
Steps to Learn Design
After understanding the learning structure in design schools, we need to implement the different resources in order to create a similar ecosystem that allows students and designer how didn’t get the chance to get a design education to learn design based on the available learning resources around them. Below are a number of steps that can be implemented altogether in order to achieve their goal to learn design:
Step1: Explore Different Design Fields
The design is a very wide discipline with different fields including but not limited to fashion design, industrial design, graphic design, and interactive design. You need to decide which field you would like to take according to three main factors:
Talent and capabilities – Which field meet with your talent and interest? Which field do you like the most? and How do you see yourself after 20 years in a specific field?
The available opportunities – What are the opportunities to work in a specific field? and How competitive the field is? and how the other factors such as the location, culture, and environments may help you to excel in the field?
In order to answer the above questions, you need to explore different fields and how it is like to work in this specific field. This can be achieved by asking experts around or through social networks. This step helps you to make a decision about the design field that you need to study and build your plan according to it.
Recommended book:
Step 2: Find a Mentor
The core behind the academic degrees is the mentorship. Professors’ role is to help students and mentor them over the course of their learning path. Finding a mentor with experience in the selected design field from the previous aids you through advice and help during your learning path. The role of the mentor may extend to help you to evaluate your work, put a learning plan, and find opportunities.
While finding a mentor is very challenging task, it is an essential one in order to get guide you through the learning process as you will notice in the following steps.
Step 3: Start by the Theory and Practice it
Many students told me that they know the tool but they don’t know how to implement it to visualize ideas or do projects. The reason for this is that many of them didn’t get the chance to understand the theory properly. For example, without learning the color theory, it may be hard to find create a color scheme for your next product design. Also, without learning the gestalt principles, you will not be able to build a coherent design layout.
There are many online resources that can help you to learn design principles and theories including books, video tutorials, and MOOCs platforms. Along with completing each resource, you need to practice it and share the work with your mentor to evaluate it and give advice. As you move forward, you should be able to understand the different design-related theories and practice it in different materials.
Examples for MOOCs courses:
While the design principles are the same in all fields, there are some topics that may be needed in a specific field. Therefore, ti is good ideas to discuss and identify with your mentor the theoretical knowledge related to your chosen niche.
Recommended books about design principles:
- Universal Principles of Design
- The Non-Designer’s Design Book (4th Edition)
- Layout Essentials: 100 Design Principles for Using Grids (Design Essentials)
- The Design of Everyday Things: Revised and Expanded Edition
Step 4: Learn the Proper Design Tools
Once you learned the theory or started to learn the theory, it is the time to learn the tools related to the chosen design discipline. For example, if you would like to learn industrial design, then you need to acquire a number of skills such as working with CAD applications and physical materials that help you to turn your ideas into prototypes. Digital design tools can be easily learned online. However, doing workshops and learning groups help you to develop your skills and share knowledge with others students.
It’s very important to choose your learning resource carefully in order to make sure that the information provided to you is correct and in a good form to avoid any time lose with your are learning specific skills.
Step 5: Observe, Observe, and Observe
One of the most important design tip to develop your visual experience is to observe. The design is all around us, observing different product ideas, how they are designed, and how the designers solved different problems will help you to inspire ideas and find a solution to your design challenges.
The real life around us, as well as the Internet, can help you to get access to millions of ideas that you can check, evaluate, and learn from it. You can use the observation to see how the theories and the tools are used in real world.
Step 6: Evaluate Your Progress
Evaluating your project and progress is essential to determine your exposure to the knowledge. While many students share the work with their peers to get feedback, this can’t be considered evaluation because it requires someone with higher experience and knowledge to evaluate your work. This one is your mentor. After learning a specific topic or tool, try to apply it in a project example. For instance, Once you learned Indesign, start by making a book design project. This will help you to merge between the theory and practice in one project that can be shared with your mentor to give you advice and comments.

The evaluation process is very important as it determines how solid is your knowledge. While this is managed by the academic grading, you need to develop a self-evaluation sense that can help you to understand your real knowledge of each design topic.
Step 7: Build a Professional Portfolio
Over the course of the learning path above, you should develop practice projects that can be suitable for your portfolio. It is important to build a professional portfolio that represents your best work and provide a proof of your skills. There are different platforms for designers such as Behance, Dribble, DeviantArts, and others. You can use these platforms to promote your work. While you build your portfolio, it is important to note that clients need to see real projects such as mobile app design, website design….etc. Practice examples and fraction work is not something that interests the clients to see.
Step 8: Get an Internship or Training
After preparing your skills and portfolio, it is the time to start real-life practice by searching for intern positions. The intern positions are offered by many companies to find new designers who would like to learn in exchange for doing projects for cheap compensation. You can find intern opportunities in local companies, search on the Internet, or freelancing websites where you can find remote clients to work for.
While the design schools are important to build designers’ skills and experience to prepare them for the market, there is still a lack of designs education and the current high tuition stands in front of many designers to fulfill their passion for learning design. The alternative learning sources such as the MOOCs and online resources can help them to learn design. However, this should be part of a learning plan to merge between both theory and practice.
The above steps can help students and designers to develop a coherent learning plan based on mentorship and evaluation for their work. These steps aim to fill the gaps related to missing part of the knowledge or focusing on part of the learning knowledge such as focusing on the tools rather than the theory. They can be applied in different design fields.






