How to Evaluate Design Ideas
Design and innovation play an essential role in today’s business success through fueling an organization’s future with creative ideas that in turn, will help maintain superiority in market competition. Investing in business ventures and start-up ideas are other reason for companies to focus on creative ideas and analyze their potential success in the market.
Designers, design managers and educators also need an evaluation process when selecting creative ideas or different design layouts for creative projects. In order to achieve the best output of the selection process, an evaluation methodology should be considered to make sure that the selected creative or design idea is the best choice to achieve the company’s target.
Unlike evaluative business plans or marketing research which deal with statistics, numbers and/or charts, reviewing creative ideas is more complicated as it focuses on the potential success of initial starting ideas. The evaluation methods helps in reviewing a large number of ideas in order to reach the one that is most likely to succeed in the market.
The evaluation method ensures putting the right team in the selection process and understands the problems potentially inherent in a creative idea and seeks to correct them during the implementation process.
Design Evaluation Methods
Mainly, there are three methods that help in evaluating design ideas; pass-fail evaluation, evaluation matrix and SWOT analysis. These methods can be implemented individually or in a sequence-based number of steps on the number of creative ideas and the type of the evaluation required.
Pass-fail evaluation method
This is the first method and can be applied for evaluating large number of ideas based in a simple acceptance or rejection question. Before going into in-depth evaluation methods, this basic step allows eliminating the ideas that do not fit with the basic project requirements such as the budget and target audiences. This method allows reviewing large number of ideas in a short time due to its simple decision-making process based on prime criteria. The criteria can include questions such as:
- Does the idea comply with company strategy? (Yes/No)
- Does it talk the company target audience? (Yes/No)
- Does the idea budget acceptable? (Yes/No)
Although there can be a large number of ideas reviewed in this method, accurate evaluations should be taken into consideration as a priority in order to avoid eliminating good ideas with potential success possibility.
Evaluation Matrix
The ideas that pass through the first method go through the evaluation matrix method. In some cases, the submitted ideas for acceptance are just a few ideas, then when submitted to the evaluation process, the reviewers can skip the first methods and transition directly to this step.
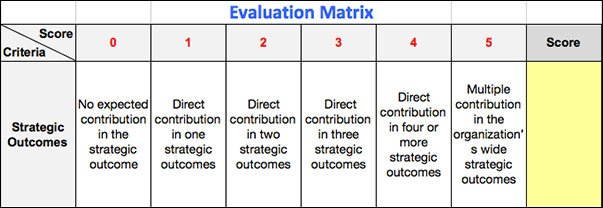
In this method, the reviewers compare the ideas with a specific matrix or set of criteria. The criteria can includes the following:
- The idea contribution in company’s overall strategic outcome
- The idea’s potential impact
- Expected stakeholders
- Expected budget to apply the idea
- Timelines to implement the idea
A specified score is given to each criterion. For example the idea contribution in company’s strategic outcome can include the following score set:
- Score 0: No expected contribution in the strategic outcome
- Score 1: Direct contribution in one strategic outcomes
- Score 2: Direct contribution in two strategic outcomes
- Score 3: Direct contribution in three strategic outcomes
- Score 4: Direct contribution in four or more strategic outcomes
- Score 5: Multiple contribution in the organization’s wide strategic outcomes
The comparison factors reflect the project requirement using a score rate. This score measures the potential success of the idea based on a number of factors. After the evaluation process is accomplished, a total score number is assigned to each idea. Each evaluator provides feedback about the idea, which can also be used to improve it.
SWOT analysis
The SWOT analysis refers to the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats of the idea as projected into the marketplace. This type of evaluation seeks to extend the reviewer vision to evaluate the idea based on the four factors, which predicts the potential success of the idea in the market based on the market related factors.
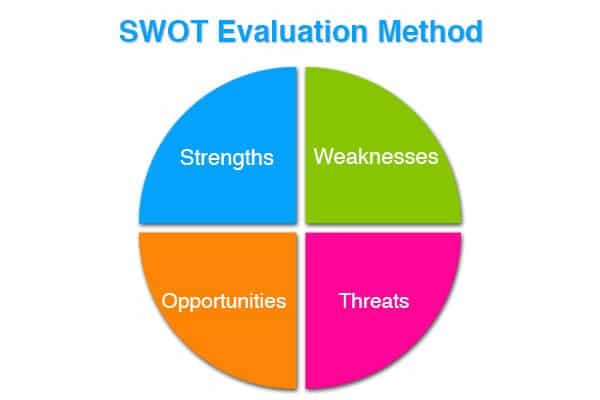
This analysis stage helps evaluating the idea based on the four SWOT factors such as questions to analyze idea’s strengths:
- What are the idea’s advantages?
- What can the idea be successful in?
- What are the current existing idea resources?
- How others may see the strength of the idea?
Questions to analyze the idea’s weaknesses:
- How can the idea can be improved?
- What does the idea lack in term of experience, team and resources?
- What can prevent the idea from success?
- How do others see the idea in terms of weaknesses?
Questions to analyze the idea’s opportunities:
- What opportunities does the idea have in the market?
- How the company can help the idea to succeed?
Questions to analyze the idea’s threats:
- What are the obstacles that face the idea?
- Do the idea weaknesses represent any thread to its success?
- What are the financial problem that may face the idea?
Approval and Implementation
Once the ideas go through the above three methods, it becomes ready to be taken to the next stage and implemented in the development process. This stage starts with creating the wireframe for the product or the design in order to have visual shape for it. Once the wireframe is reviewed and approved by different reviewers, the idea can be put into a full production development process.
The above evaluation methods help review and select the design ideas that are most suitable for market competency in order to achieve the company goals. These evaluation methods can be used all together or in sequence starting from the first method until the third one or individually based on the company’s objectives and/or requirements.
Related articles:
- How Design Contributes to Strategic Thinking Inside the Organization
- Estimating a Design Project Budget
- How Does Apple’s Design Process Work?






