How Design Thinking Approaches Problems
Design thinking is widely known as a strategy to successfully address complex problems and build products that address consumers’ needs. Many word-leading design companies, such as Apple, Microsoft, IKEA, Lego and others, have achieved success through applying design thinking in their product development process.
While there are similarities between the design thinking process and other development process and marketing process, the question is: what makes the design thinking unique? Why has it been able to take companies, such as Apple in 1997 and Lego between 1993 2004, from failure to success? Answering these questions requires us to take a step back and look not only at the process stages, but at the core strategies that are approached in the design thinking process. While there are many approaches to be addressed in the development process, such as with regards to technology or marketing, design thinking has different approaches, which focus on the user’s needs, solving problems, achieving innovation, and so on.
Understanding the core approaches of the design thinking process helps both designers and non-designers to use the process properly and to ensure that these approaches are met in the different development stages.
Related articles:
- The Six Systems Thinking Steps to Solve Complex Problems
- What Kills Design Thinking?
- If You Believe that Design Thinking is a Waste of Time, You’re Doing It Wrong
User-Centric Approach
Design thinking is defined as a problem-solving methodology that is used to address people’s needs and provide desirable solutions for their everyday problems. Accordingly, a user-centric culture is the core of any of the design thinking models and should be maintained in every stage in the design process. The user-centric approach ensures that the final product or design has one ultimate goal; that is to say, the goal of solving the user problem in a desirable and usable way (think of IKEA products, for example). The design strategy in IKEA, Democratic Design, aims to achieve a number of factors that target consumer satisfaction: good form, usable function, high quality, affordable prices, and sustainable products.
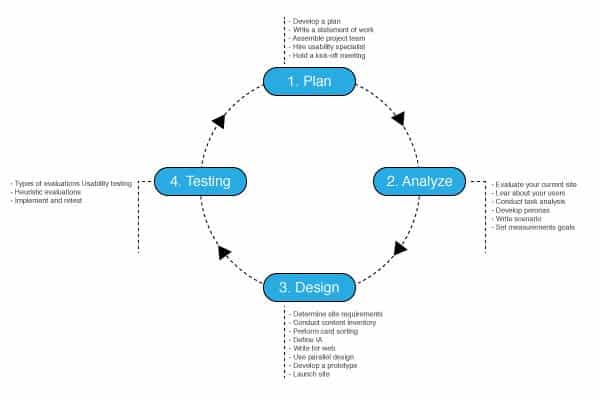
Designers focus on their user needs while designing a specific product as this the only way to achieve success. If the product is missing any of the factors in IKEA’s strategy above, it will not succeed in achieving consumer satisfaction, which leads to direct product failure. Therefore, the design thinking process tends to ensure this approach is achieved through number of methods such as user testing, validation, and multiple iterations between different stages. In order to achieve this understanding, designers are required to conduct deep user research methods such as the Journey Map in order to collect the information that contributes to understanding the user needs.
Problem-solving approach
Design in its core is a problem-solving method as designers come up with solutions for our everyday problems in order to make our lives easier. Sadly, many designers do not learn this approach in schools, which can affect their design outcome after they graduate and join a professional career. Unlike art, designers need to implement design tools and principles in order to provide better user experience for their audience. In the design thinking process, this approach should be clearly defined by the second stage of product development process. For example, in the Double Diamond diagram presented by the British Council, the first stage (Discover) allows designers to investigate the problem that needs to be addressed and to collect enough information regarding it. The second stage (Define) organizes the collected information and allows designers to analyze it to clearly define it for the next Development stage.
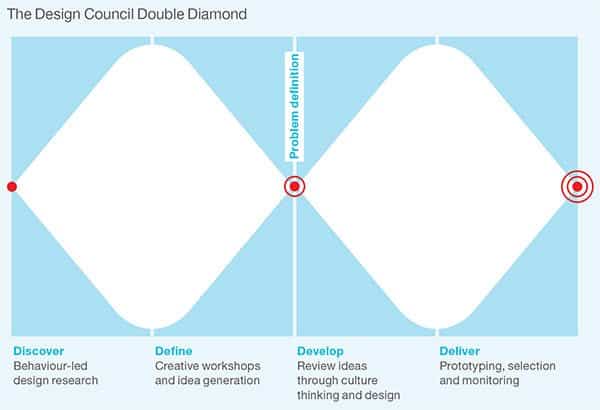
Another example is the Stanford D.School design thinking process, which includes the first three stages of Empathize, Define, and Ideate. Those three stages focus on investigating and defining the problem that needs to be addressed and how it will be solved in the final product or service. Many design tools can be used to find solutions for problems, such as the System thinking, CATWOE, Cause and Effect Diagram, and TRIZ.
In relation to the problem-solving approach, prototyping is considered one of the most important stages in all the design thinking processes. This stage helps designers to visualize the ideas and build a better understanding of how this design might solve the user problem.
Design to Stay
Design thinking solutions are not temporary; they are meant to stay and consider the future factors in addition to the existing factors. Design future is another important approach that should be considered when developing a new product or service, and designers should have a clear awareness of the trending technologies and how they will affect the produced design or the proposed solution.

Products should be designed for the future as well as the present as consumers are expected to use the product for years after buying it. Designing with the future technology in mind helps designers to address not only today’s problems but also the future problems that may face consumers. The same approach should likewise be applied in solving problems. Designers should not think in the short term, but also the long term. One of the design thinking tools that addresses this approach is the 8D problem-solving strategy which was first coined by Henry Ford. In this tool, the design team provides a temporary solution for problems while considering developing a permanent solution that is targeted for long-term usage.
Empathic Approach
Empathy means that designers should put themselves in the consumer shoes. They are not only required to think about the consumer needs, but also their feeling about the product or competitive products. Collecting information about the consumers’ feelings about the product contribute to building the so-called emotional design; the design that address users’ emotions in addition to their physical needs.
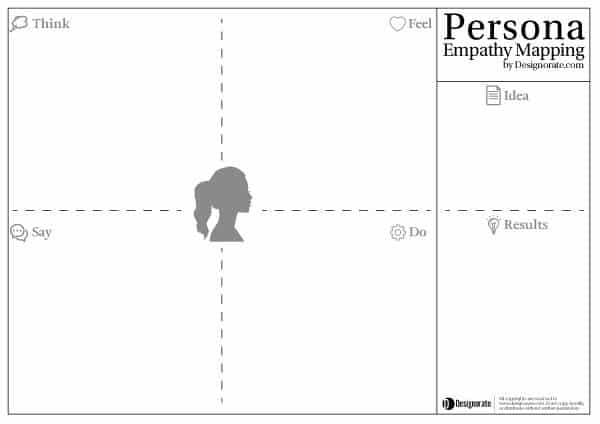
One of the tools that can help designers to define these emotional feelings about the product is the Persona Empathy Mapping which tends to create a persona that represents the consumer feelings such as how they think and feel, and what they do and say, about the product.
Pattern-Based Thinking
Design is represented in a complete picture of the product or the situation as our consumers see the design as a whole rather than its parts. Therefore, designers are required to think about their design as a whole product rather than individual components. For example, designers should focus on the product based on different factors such as form, function, quality, used materials, content, and the final price. Designers should also think about how their products will be used during the consumer life in the context of other items and circumstances. For example, how might a new car design integrate with the roads regulation in any given country? One cannot simply design a left-driven car for UK streets while ignoring other parts of the global market. Understanding methods such as the Systems Thinking theory can help designers to build a bigger picture of the product and how it will be integrated with the environment around it.
Innovation-based Thinking
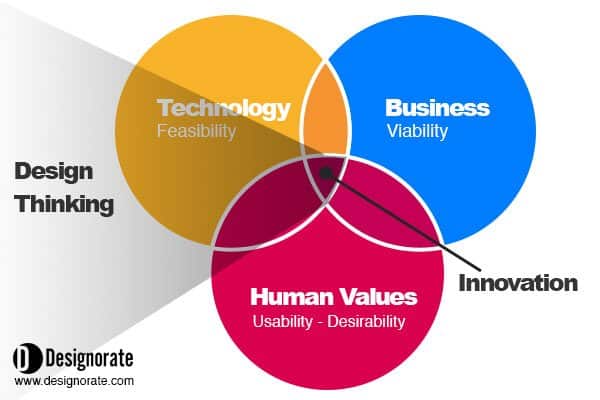
There is a strong relation between design thinking and innovation. In actual fact, innovation models such as the Stage-Gate can be easily integrated with the different design thinking methods to improve the design team capability to foster innovation. Based on the IDEO, innovation lies in the interaction of three factors: user desirability, business viability, and technology feasibility. The design thinking processes can help designers to achieve those three factors and subsequently reach innovation. Additionally, many tools such as brainstorming, mind mapping, and TRIZ problem solving can be used to achieve different types of innovation sustaining innovation, disruptive innovation, and breakthrough innovation.
While there are many processes that may look similar to the design thinking process, the approaches that are used to address design thinking make these processes more unique and desirable. Some development processes are technology-biased or aim to increase the salability, or make a need for the product. The design thinking process, unlikely, aims to address existing consumers’ needs, solving their problems, and understanding their feelings about the product. Additionally, design thinking focuses on the whole system rather than its individual parts and targets achieving innovation with considering the future needs of the end consumers. Design thinking provides a unique framework to address the above approaches which have been shown to achieve success in the existing design industry.






All the above mentioned tools , methodologies are regular practices in industrial designer. Now with the digital era we are re looking at all of them in a new perspective.Similar innovative case studies of Marico industries, Titan watches are also worth noting.
This is true Shetall. The IT and software design industry needs more investigation to build an integrated design thinking model that can be deployed in the software development process. Some companies like IBM and Microsoft already developed their own process though.